Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMMQ8ZG)
| Drug Name |
Furosemide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aisemide; Aldalix; Aldic; Aluzine; Anfuramaide; Aquarid; Aquasin; Arasemide; Beronald; Bioretic; Cetasix; Depix; Desal; Desdemin; Dirine; Disal; Discoid; Disemide; Diural; Diurapid; Diurin; Diurolasa; Diusemide; Diusil; Diuzol; Dranex; Dryptal; Durafurid; Edemid; Edenol; Eliur; Endural; Errolon; Eutensin; FUN; Farsix; Fluidrol; Fluss; Franyl; Frumex; Frumide; Frusedan; Frusema; Frusemid; Frusemide; Frusemin; Frusenex; Frusetic; Frusid; Fulsix; Fuluvamide; Fuluvamine; Fulvamide; Furanthril; Furanthryl; Furantral; Furantril; Furanturil; Furesis; Furetic; Furex; Furfan; Furix; Furmid; Furobeta; Furocot; Furodiurol; Furodrix; Furomen; Furomex; Furorese; Furosan; Furose; Furosedon; Furosemid; Furosemida; Furosemidu; Furosemidum; Furosemix; Furoside; Furosifar; Furosix; Furoter; Furovite; Fursemid; Fursemida; Fursemide; Fursol; Fusid; Golan; Hissuflux; Hydrex; Hydro; Hydroled; Impugan; Jenafusid; Katlex; Kofuzon; Kolkin; Kutrix; Lasemid; Lasex; Lasiletten; Lasilix; Lasix; Laxur; Lazix; Liside; Logirene; Lowpston; Lowpstron; Luscek; Macasirool; Marsemide; Mirfat; Mita; Moilarorin; Myrosemide; Nadis; Nelsix; Novosemide; Odemase; Odemex; Oedemex; Prefemin; Profemin; Promedes; Promide; Protargen; Puresis; Radisemide; Radonna; Radouna; Retep; Rosemide; Rosis; Rusyde; Salinex; Salix; Salurex; Salurid; Seguril; Selectofur; Sigasalur; Spirofur; Synephron; Transit; Trofurit; Uremide; Uresix; Urian; Uridon; Uritol; Urosemide; Vesix; Yidoli; Zafimida; FUROSEMIDE USP; Fu sid; Furosemide Monohydrochloride; Furosemide Monosodium Salt; Furosemidu [Polish]; Lasix Retard; Lasix Special; Less Diur; Polysquall A; Sal diureticum; F0182; F4381_SIGMA; LB 502; Aisemide (TN); Apo-Frusemide; Apo-Furosemide; Beronald (TN); Desdemin (TN); Discoid (TN); Diumide-K; Diural (TN); Diurapid (TN); Dryptal (TN); Durafurid (TN); Errolon (TN); Eutensin (TN); Frudix (TN); Frusetic (TN); Frusid (TN); Fulsix (TN); Fuluvamide (TN); Furesis (TN); Furix (TN); Furo-Basan; Furo-puren; Furomide M.D; Furosedon (TN); Furosemida [INN-Spanish]; Furosemide (mita); Furosemidum [INN-Latin]; Hoe-058A; Hydro-rapid; Impugan (TN); Katlex (TN); LB-502; Lasilix (TN); Lasix (TN); Lodix (TN); Lowpston (TN); Macasirool (TN); Mirfat (TN); Neo-renal; Nicorol (TN); Odemase (TN); Oedemex (TN); Profemin (TN); Rosemide (TN); Rusyde (TN); Salix (TN); Salix (brand of furosemide); Trofurit (TN); Urex (TN); Urex-M; Apo-Furosemide (TN); Furo-Puren (TN); Furomide M.D.; Furosemide [USAN:INN:JAN]; Hydro-rapid(TN); Lasix, Frusemide, Furosemide; Furosemide (JP15/USP/INN); Chlor-N-(2-furylmethyl)-5-sulfamylanthranilsaeure; Chlor-N-(2-furylmethyl)-5-sulfamylanthranilsaeure [German]; 2-Furfurylamino-4-chloro-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid; 4-Chloro-5-sulfamoyl-N-furfuryl-anthranilic acid; 4-Chloro-N-(2-furylmethyl)-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid; 4-Chloro-N-furfuryl-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid; 4-chloro-2-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid; 4-chloro-2-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)amino]-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Diuretics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
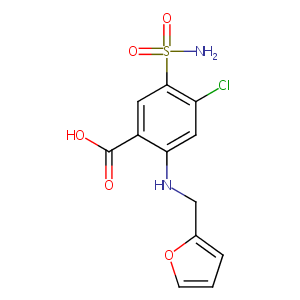 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 330.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Furosemide
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Furosemide (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4839). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Furosemide FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Retevmo (selpercatinib) capsules | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Andreasen F, Mikkelsen E: Distribution, elimination and effect of furosemide in normal subjects and in patients with heart failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Aug 17;12(1):15-22. doi: 10.1007/bf00561400. | ||||
| 6 | Nichols DJ, Muirhead GJ, Harness JA: Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after single oral doses in healthy male subjects: absolute bioavailability, food effects and dose proportionality. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;53 Suppl 1:5S-12S. | ||||
| 7 | Furosemide - FDA Label | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 10 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 11 | Update of diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Am J Ther. 2007 Mar-Apr;14(2):154-60. | ||||
| 12 | Peptide transporter substrate identification during permeability screening in drug discovery: comparison of transfected MDCK-hPepT1 cells to Caco-2 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Apr;30(4):507-18. | ||||
| 13 | Interactions of human organic anion transporters with diuretics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Mar;308(3):1021-9. | ||||
| 14 | Effects of cytochrome P450 inducers and inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous furosemide in rats: involvement of CYP2C11, 2E1, 3A1 and 3A2 in furosemide metabolism. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;61(1):47-54. | ||||
| 15 | Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Nov;32(11):1201-8. | ||||
| 16 | Bucolome, a potent binding inhibitor for furosemide, alters the pharmacokinetics and diuretic effect of furosemide: potential for use of bucolome to restore diuretic response in nephrotic syndrome. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Apr;33(4):596-602. doi: 10.1124/dmd.104.002782. Epub 2005 Jan 7. | ||||
| 17 | Secondary pulmonary hypertension: haemodynamic effects of torasemide versus furosemide. Clin Drug Investig. 2008;28(1):17-26. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200828010-00003. | ||||
| 18 | Multichannel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry cocktail method for comprehensive substrate characterization of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 transporter. Pharm Res. 2007 Dec;24(12):2281-96. | ||||
| 19 | Inhibition profiling of human carbonic anhydrase II by high-throughput screening of structurally diverse, biologically active compounds. J Biomol Screen. 2006 Oct;11(7):782-91. | ||||
| 20 | A Gene Expression Biomarker Predicts Heat Shock Factor 1 Activation in a Gene Expression Compendium. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 Jul 19;34(7):1721-1737. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00510. Epub 2021 Jun 25. | ||||
| 21 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 22 | Antihypertensive drugs clonidine, diazoxide, hydralazine and furosemide regulate the production of cytokines by placentas and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal pregnancy. J Hypertens. 2006 May;24(5):915-22. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000222762.84605.03. | ||||
| 23 | [Effects of 4-hour erect posture and furosemide on the blood level of atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with primary arterial hypertension]. Przegl Lek. 1990;47(3):332-4. | ||||
| 24 | Leary WP, Reyes AJ "Drug interactions with diuretics." S Afr Med J 65 (1984): 455-61. [PMID: 6701709] | ||||
| 25 | Brown DD, Dormois JC, Abraham GN, et al "Effect of furosemide on the renal excretion of digoxin." Clin Pharmacol Ther 20 (1976): 395-400. [PMID: 975715] | ||||
| 26 | Chrysos G, Gargalianos P, Lelekis M, Stefanou J, Kosmidis J "Pharmacokinetic interactions of ceftazidime and frusemide." J Chemother 7 Suppl (1995): 107-10. [PMID: 8904125] | ||||
| 27 | Athlin L, Domellof L, Holm S "Gentamicin treatment in severe surgical infections: serum levels, interactions, toxicity and efficacy." Acta Chir Scand 147 (1981): 225-30. [PMID: 7034430] | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Lipworth BJ, McDevitt DG, Struthers AD "Prior treatment with diuretic augments the hypokalemic and electrocardiographic effects of inhaled albuterol." Am J Med 86 (1989): 653-7. [PMID: 2729315] | ||||
| 30 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Low magnesium levels can be associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs).". | ||||
| 31 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Skelid (tilundronate). Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 33 | Muller FO, Schall R, Devaal AC, Groenewoud G, Hundt HKL, Middle MV "Influence of meloxicam on furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1995): 247-51. [PMID: 7589049] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Savella (milnacipran). Forest Pharmaceuticals, St. Louis, MO. | ||||
| 35 | Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424] | ||||
| 36 | Andrews C, Pinner G "Postural hypotension induced by paroxetine." BMJ 316 (1998): 595. [PMID: 9518913] | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Aptiom (eslicarbazepine). Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Marlborough, MA. | ||||
| 38 | Arnold W, Nadol JB Jr, Weidauer H "Ultrastructural histopathology in a case of human ototoxicity due to loop diuretics." Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 91 (1981): 399-414. [PMID: 6973908] | ||||
| 39 | Dean S, Kendall MJ, Potter S, Thompson MH, Jackson DA "Nadolol in combination with indapamide and xipamide in resistant hypertensives." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28 (1985): 29-33. [PMID: 3987783] | ||||
| 40 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 41 | Burnakis TG, Mioduch HJ "Combined therapy with captopril and potassium supplementation: a potential for hyperkalemia." Arch Intern Med 144 (1984): 2371-2. [PMID: 6391404] | ||||
| 42 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Zometa (zoledronic acid). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 45 | Cohen J "Long-term efficacy and safety of terazosin alone and in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am Heart J 122 (1991): 919-25. [PMID: 1678923] | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Orap Tablets (pimozide). Gate Pharmaceuticals, Sellersville, PA. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Clozaril (clozapine). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | Antonelli D, Atar S, Freedberg NA, Rosenfeld T "Torsade de pointes in patients on chronic amiodarone treatment: contributing factors and drug interactions." Isr Med Assoc J 7 (2005): 163-5. [PMID: 15792261] | ||||
